Cholestasis Alters miR-34c-5p Expression in the Testes of Male Wistar Rats, Gene, Cell and Tissue
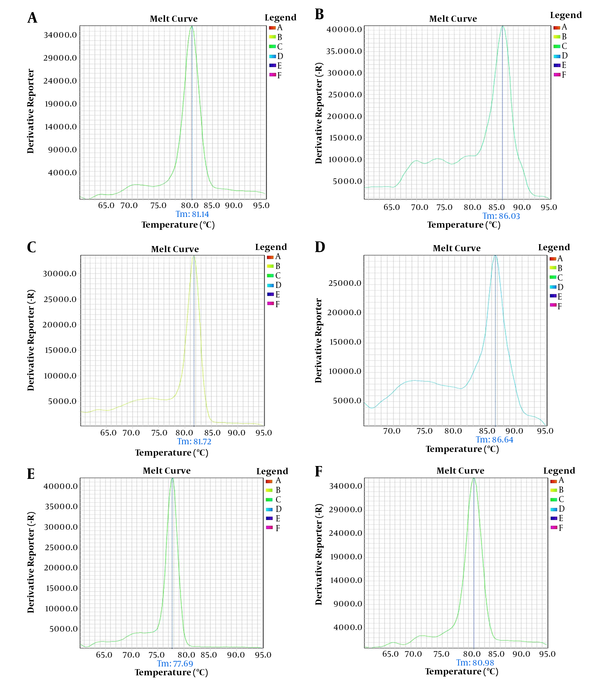
Background: Cholestasis is a pathophysiological condition, significantly reducing spermatozoa production. MiR-34c is highly expressed in adult male testicles and controls different stages of spermatogenesis. Objectives: Here, we aimed to investigate miR-34c expression in the testes of rat models of cholestasis. The expressions of THY-1, FGF-2, and CASP-3 genes, that are targeted by mirR-34c were also investigated. Methods: Cholestasis was induced in six adult rats via bile duct ligation. Four weeks after cholestasis induction, sera and testicular tissues were collected for further examinations. The levels of liver enzymes were measured using the ELISA. The structure of the testes was evaluated by histological examination. Total RNA was extracted from testes using a special kit and converted to cDNA. The expressions of miR-34c-5p, THY-1, FGF-2, and CASP-3 genes were determined by Real-Time PCR. Results: The serum levels of ALP, AST, and ALT were significantly elevated in the rat models of cholestasis (P < 0.001). Real-Time PCR revealed that the expressions of miR-34c-5p, THY-1, and FGF-2 genes decreased while CASP-3 gene was upregulated in the testes of cholestatic animals (all differences were significant at P < 0.05). Conclusions: Our study indicated that cholestasis was associated with reduced expression of miR-34c and altered expression of its target genes in the testis. Our results highlight the potential effects of cholestasis, a hepatobiliary disease, on testicular tissue function and male fertility.

Hanieh JALALI, Professor (Assistant), Ph.D, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Department of Animal Science Biology

LDLR heterozygous deletion reduces hamster testicular cholesterol toxicity via AMPK/Sirt1/PGC-1α pathway - ScienceDirect
Gene, Cell and Tissue
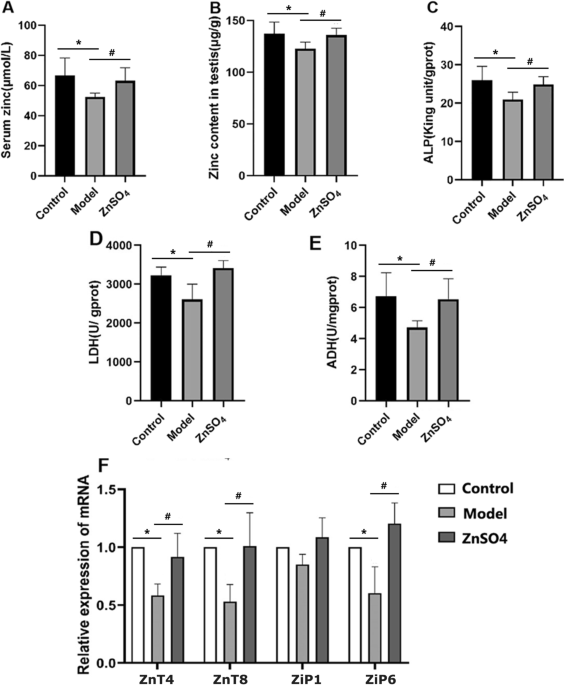
Zinc Ameliorates Tripterygium Glycosides–Induced Reproductive Impairment in Male Rats by Regulating Zinc Homeostasis and Expression of Oxidative Stress–Related Genes

Nanos2 was upregulated by miR-34c in mouse model of cryptorchidism. a

Homa KOUCHESFEHANI, phD, Kharazmi University, Tehran, KHU, Animal Biology

IJERPH October-1 2022 - Browse Articles

Differentially expressed microRNA in testicular tissues of hyperuricaemia rats - Ma - 2021 - Andrologia - Wiley Online Library

Delay in puberty indices of Wistar rats caused by Cadmium. Focus on the redox system in reproductive organs - ScienceDirect

miR-125a-5p post-transcriptionally suppresses GALNT7 to inhibit proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer cells via the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway, Cancer Cell International

Cadmium exposure-induced rat testicular dysfunction and its mechanism of chronic stress - ScienceDirect

Mouse model of cryptorchidism. a The normal (red circle) and

Mouse model of cryptorchidism. a The normal (red circle) and

Hesperidin ameliorates hepatic dysfunction and dyslipidemia in male Wistar rats exposed to cadmium chloride - ScienceDirect

Prenatal bisphenol S exposure induces hepatic lipid deposition in male mice offspring through downregulation of adipose-derived exosomal miR-29a-3p - ScienceDirect