A bioelectronic mesh capable of growing with cardiac tissues for

A team of engineers led by the University of Massachusetts Amherst and including colleagues from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) recently announced in Nature Communications that they had successfully built a tissue-like bioelectronic mesh system integrated with an array of atom-thin graphene sensors that can simultaneously measure both the electrical signal and the physical movement of cells in lab-grown human cardiac tissue.
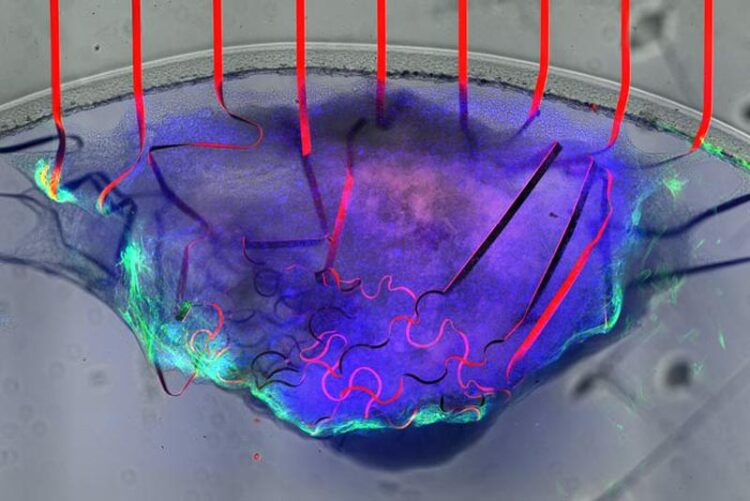
Bioelectronic mesh capable of growing with cardiac tissues

TRiCares Announces Successful Implantation of Minimally Invasive

Scientists zero in on antibodies capable of neutralizing HIV

Bioelectronic devices for cardiac tissue implantation. a) Composite for

A bioelectronic mesh capable of growing with cardiac tissues for
Engineering of Bionic Tissues The integration of electronic

New study reveals role of hippocampus in two functions of memory

Clearance of p16Ink4a+ cells: Limited effects on β-cell mass and proliferation in mice

New study links placental oxygen levels to fetal brain development
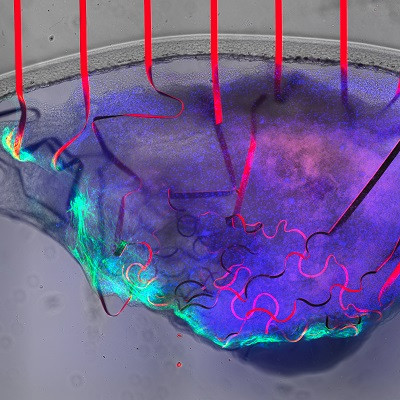
UMass Amherst Engineers Create Bioelectronic Mesh Capable of

Epicardial bioelectronic systems. (a) Conformal electronics for
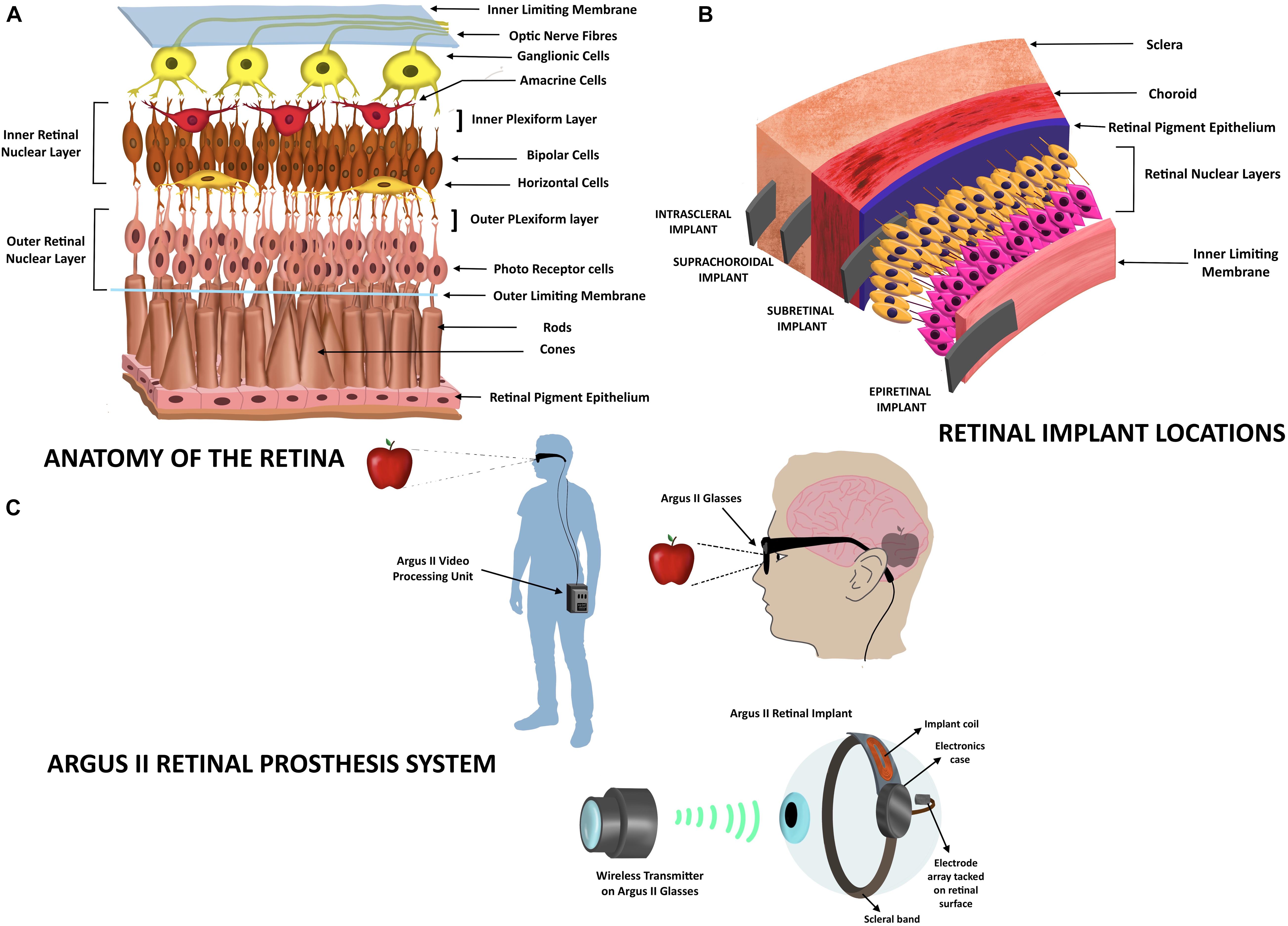
Frontiers Neurosensory Prosthetics: An Integral Neuromodulation

Microbiome studies explore why more women develop Alzheimer's disease

Physical fitness since childhood associated with cerebellar volume in adolescence: Study