The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic


Understanding the underlying molecular pathways by which Mboat7/Lpiat1 depletion induces hepatic steatosis - Journal of Lipid Research
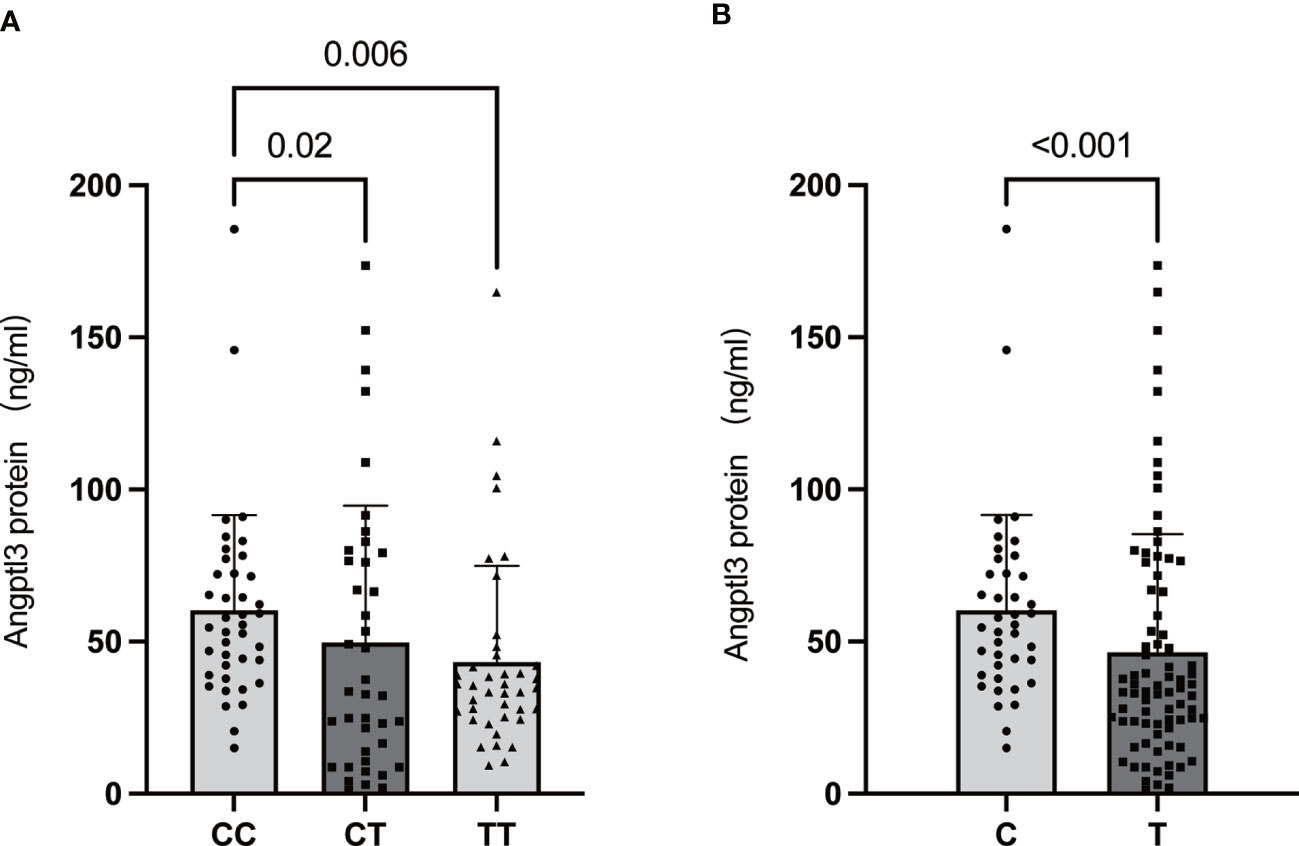
Frontiers MBOAT7 rs641738 (C>T) is associated with NAFLD progression in men and decreased ASCVD risk in elder Chinese population

Genetic Contribution to Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Prognostic Implications

Enhancing Hepatic MBOAT7 Expression Does Not Improve Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice

Genetic predisposition similarities between NASH and ASH: Identification of new therapeutic targets - JHEP Reports
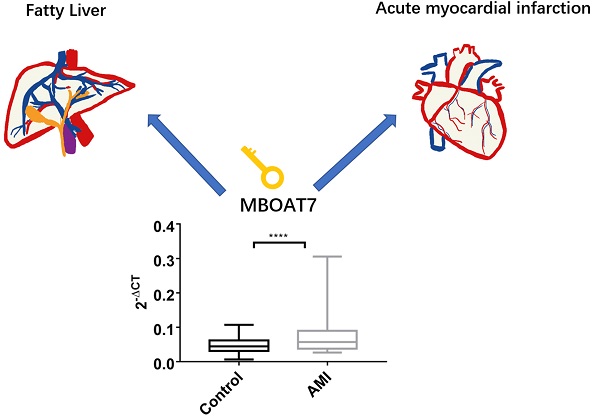
Expression of Membrane Bound O-Acyltransferase Domain Containing 7 after Myocardial Infarction and its Role in Lipid Metabolism in vitro

Investigating the Relationship Between Rare Genetic Variants and Fibrosis in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals of European Descent - ScienceDirect

PDF] A Protein‐Truncating HSD17B13 Variant and Protection from Chronic Liver Disease
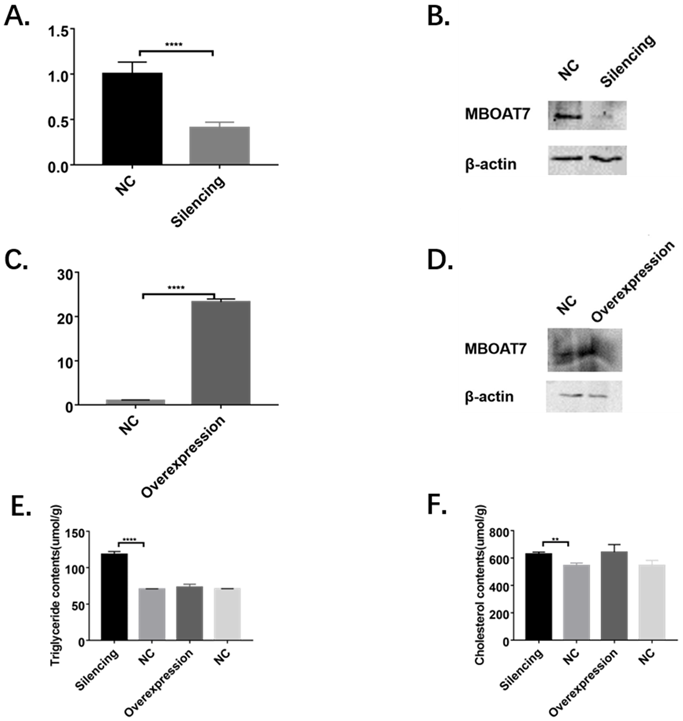
Expression of Membrane Bound O-Acyltransferase Domain Containing 7 after Myocardial Infarction and its Role in Lipid Metabolism in vitro
Risk estimation model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Japanese using multiple genetic markers

PDF) Genetic risk factors associated with NAFLD Hepatoma Research and DongYun Kim

MBOAT7 rs641738 increases risk of liver inflammation and transition to fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C

PDF] A Protein‐Truncating HSD17B13 Variant and Protection from Chronic Liver Disease
Lack of evidence supporting a role of TMC4-rs641738 missense variant—MBOAT7- intergenic downstream variant—in the Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease