Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire

Download scientific diagram | — Rear-foot inversion–eversion during walking. Throughout the entire gait cy- cle, there was a significant mean difference of 2.07 ° ± 0.29 ° between chronic-ankle-insta- bility (CAI) and control subjects. CAI subjects demonstrated more inversion than controls. from publication: Altered Ankle Kinematics and Shank-Rear-Foot Coupling in Those With Chronic Ankle Instability | Kinematic patterns during gait have not been extensively studied in relation to chronic ankle instability (CAI). To determine whether individuals with CAI demonstrate altered ankle kinematics and shank-rear-foot coupling compared with controls during walking and jogging. Case | Ankle Joint, Kinematics and Gait | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
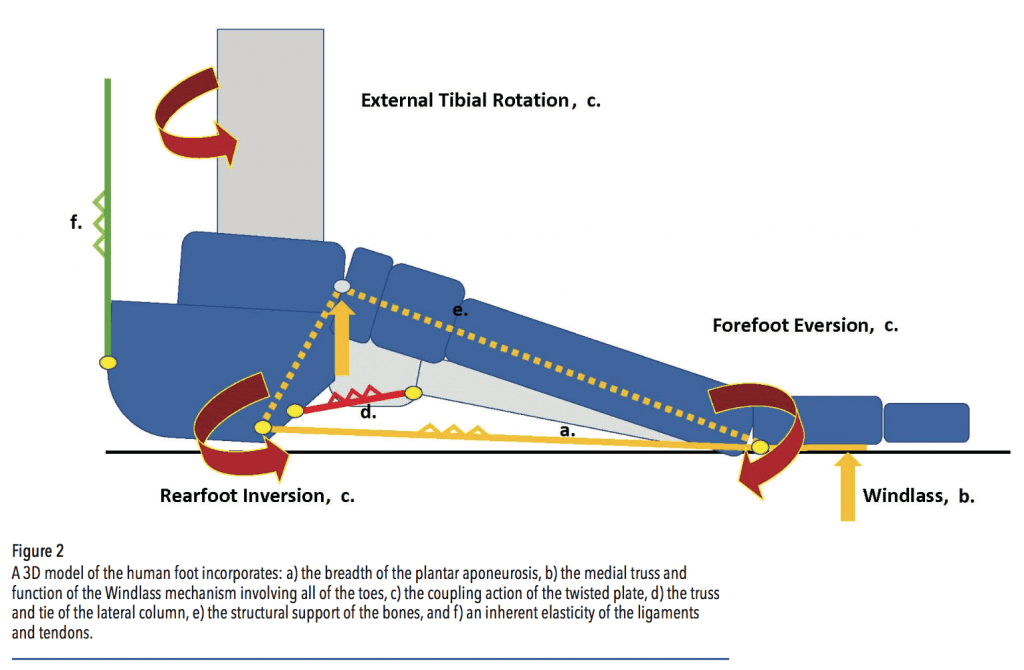
Arch Mechanics and the Plantar Fascia - Hersco Edu Center

PDF) Altered Ankle Kinematics and Shank-Rear-Foot Coupling in Those With Chronic Ankle Instability

Rear foot inversion/eversion during running relative to the subtalar
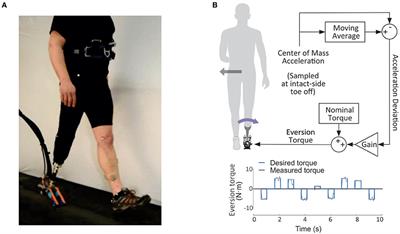
Frontiers Step-to-Step Ankle Inversion/Eversion Torque Modulation Can Reduce Effort Associated with Balance

The evaluation of the inversion/eversion of the calcaneus
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/run-off-your-heels-512698489-59601c625f9b583f180ba933.jpg)
Subtalar Joint: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment

a. Measure of forefoot on rearfoot inversion/eversion excursion. b.

Eversion of the Foot, Anatomy, Muscles & Movement - Lesson

Shank rotation during walking. Within the first 2% of the gait cycle
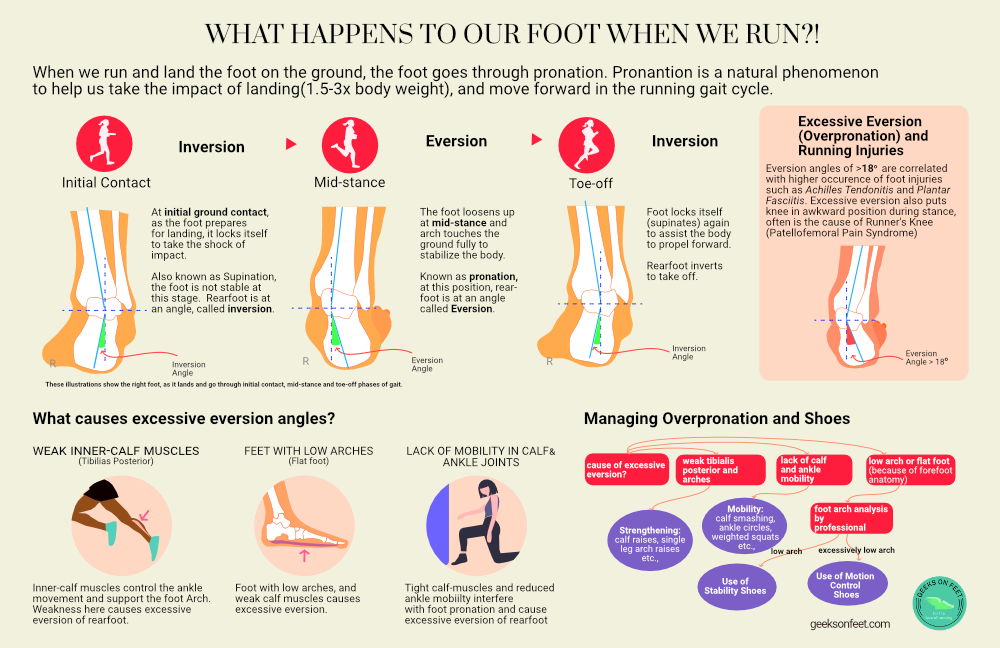
What happens to our feet when we run?!