Pathophysiology of Crohn's disease inflammation and recurrence
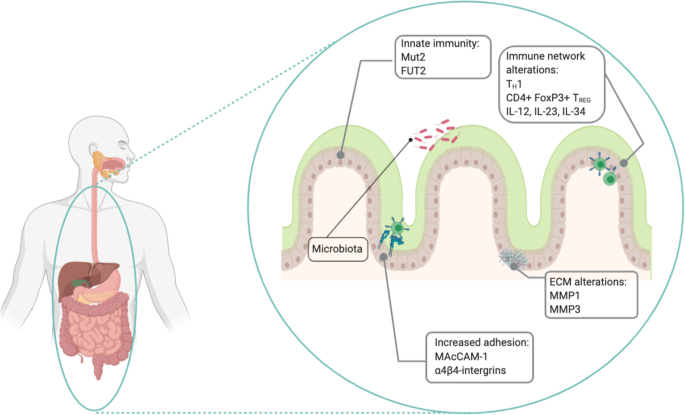
Chron’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disease, first described at the beginning of the last century. The disease is characterized by the alternation of periods of flares and remissions influenced by a complex pathogenesis in which inflammation plays a key role. Crohn’s disease evolution is mediated by a complex alteration of the inflammatory response which is characterized by alterations of the innate immunity of the intestinal mucosa barrier together with a remodeling of the extracellular matrix through the expression of metalloproteins and increased adhesion molecules expression, such as MAcCAM-1. This reshaped microenvironment enhances leucocytes migration in the sites of inflammation, promoting a TH1 response, through the production of cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α. IL-12 itself and IL-23 have been targeted for the medical treatment of CD. Giving the limited success of medical therapies, the treatment of the disease is invariably surgical. This review will highlight the role of inflammation in CD and describe the surgical approaches for the prevention of the almost inevitable recurrence.
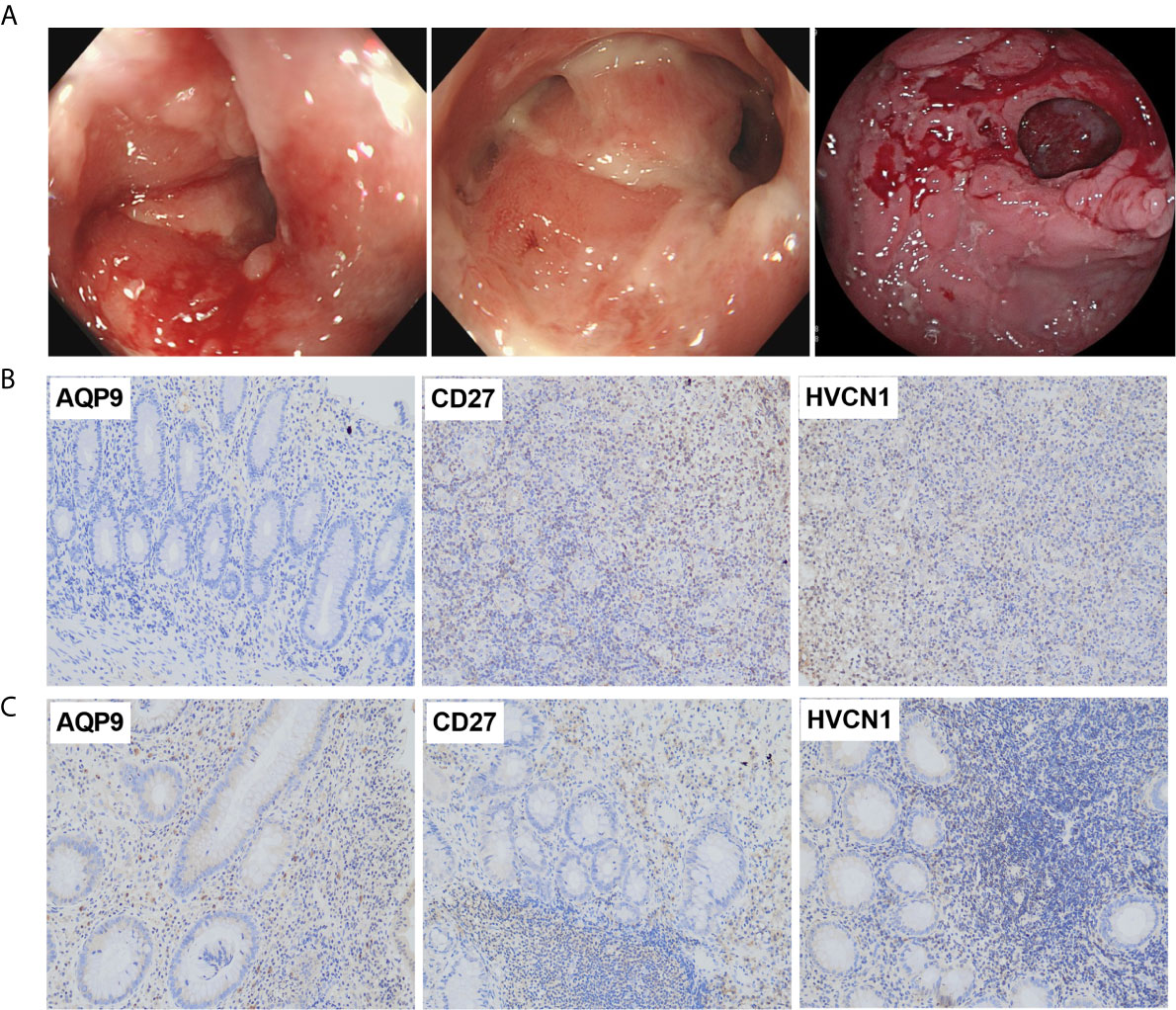
Frontiers Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Immune-Related Genes in Crohn's Disease
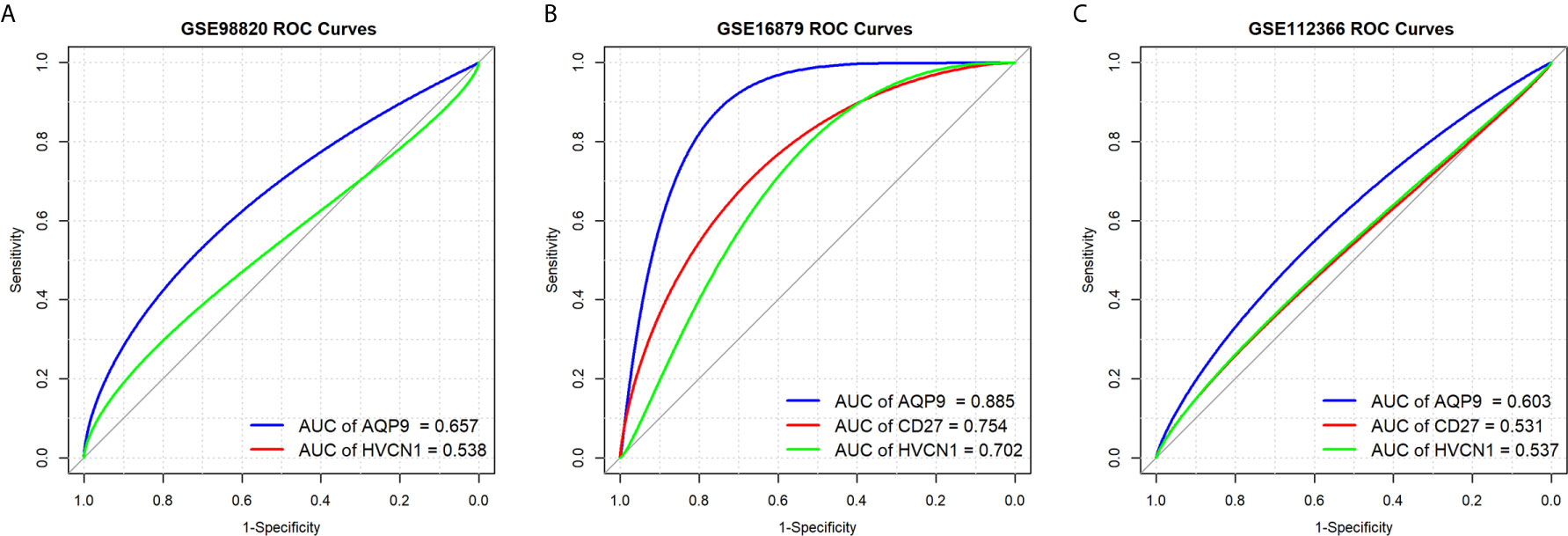
Frontiers Diagnostic and Predictive Value of Immune-Related Genes in Crohn's Disease
Crohn's Disease - Symptoms, Causes, Complications & Prevention

Medical management of fistulising Crohn's disease

Pathophysiology of Crohn's disease inflammation and recurrence, Biology Direct
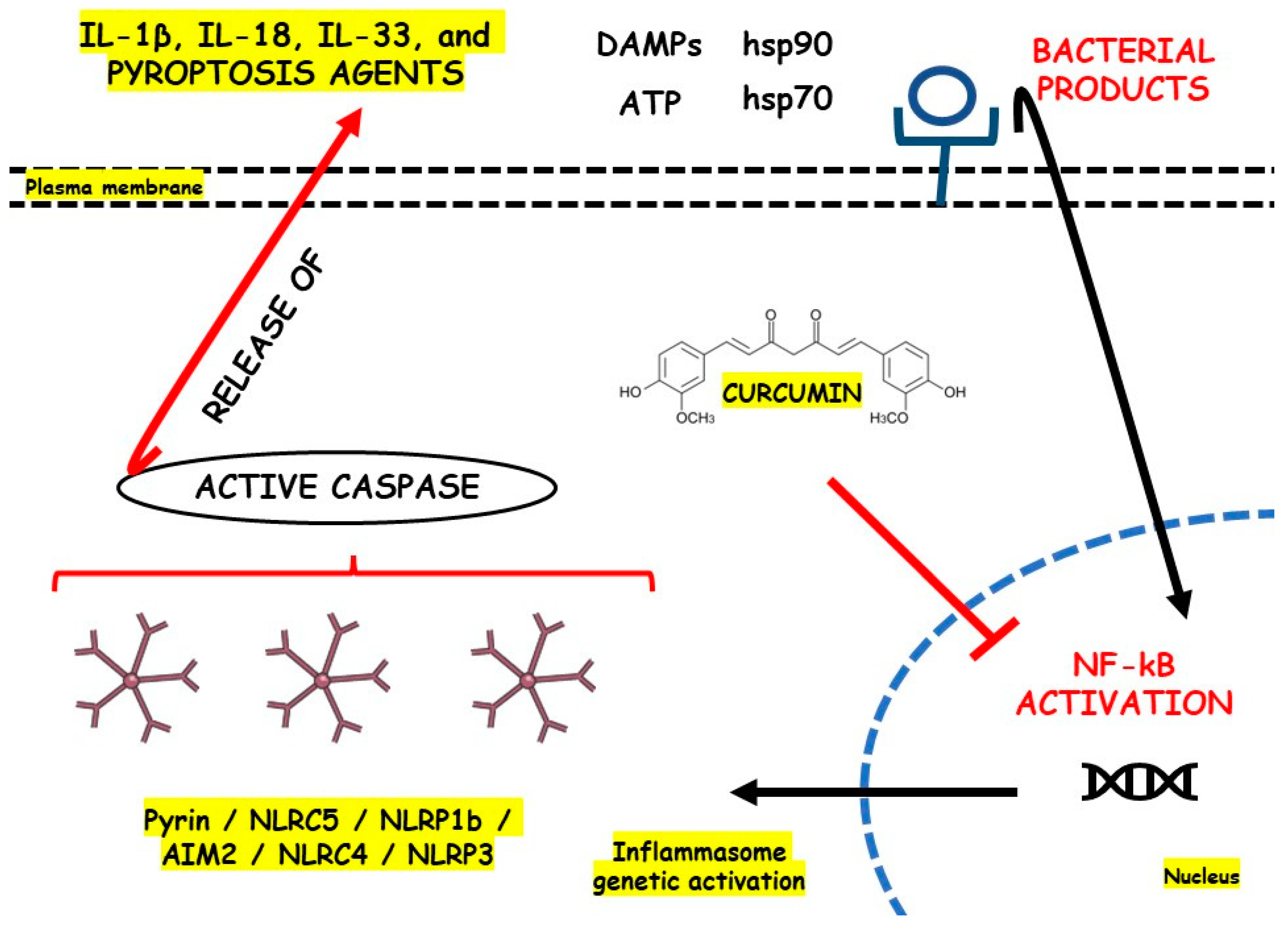
Metabolites, Free Full-Text

Pathogenesis and management of gastrointestinal inflammation and fibrosis: from inflammatory bowel diseases to endoscopic surgery, Inflammation and Regeneration

10 Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Nursing Care Plans - Nurseslabs

JCM, Free Full-Text
Crohn's disease - Wikipedia

PDF] Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease

Exploring the relationship between Faecalibacterium duncaniae and Escherichia coli in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Insights and implications - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal

Sotetsuflavone ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage-induced intestinal barrier damage via JNK and MAPK signalling - ScienceDirect