Electronics, Free Full-Text
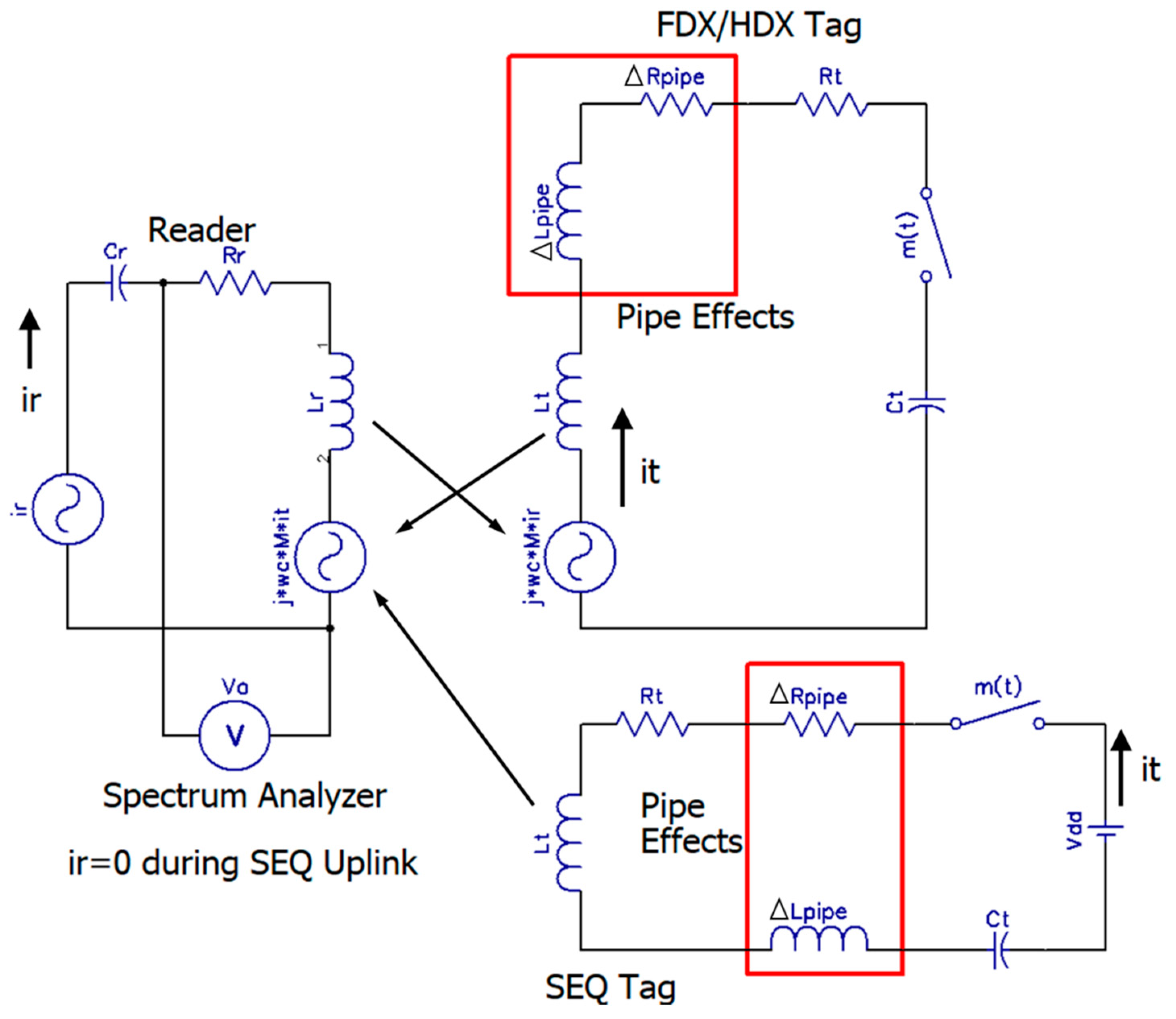
The world’s oil and gas is transported using a network of steel pipelines most of which lie underground. The length of this network in the US/Canada alone is 3.5 million kilometers. Keeping track of pipes in such a network for pipeline-health monitoring, maintenance, and logistics is an acute problem faced by pipeline-operators. Recently, radio-frequency-identification tags (RFIDs) have been proposed for tracking pipelines and even for monitoring pipeline health with additional built-in sensors. Low-cost RFID tags are wirelessly powered and battery-less. However, RFIDs do not function optimally in the presence of magnetic carbon steel pipes that are prevalent in the industry. High-frequency wireless signals also attenuate rapidly through wet soils. In this research, the use of passive RFID sensor platforms for interrogating buried pipes up to 1.25 m deep in the LF bands is proposed. Using magnetic-induction-based communication, a test-comparison between conventional full/half duplex (FDX/HDX) and sequential (SEQ) RFID schemes is detailed. Wireless measurements in the presence of an industry-standard ASTM A-53 carbon-steel pipe show a SEQ RFID offering better immunity against magnetic proximity effects of the pipe’s wall with an 8.3 dB (x6.8) improvement over a FDX/HDX RFID operating under similar conditions over a distance of 80–125 cm at which pipes are typically buried.
Popular Electronics Electronic Experimenter's Handbook 1979 : Ziff

Electronic Circuits: Fundamentals and applications

Electronics Free Full-Text Experimental Analysis Of, 47% OFF

Electronics. Free Full. Text

Electronics Shop - WordPress theme
Electronics, Free Full-Text

Free Electronics Recycling Event

Computer Music Magazine Subscription
DC/DC Converters: Devices Capable of Converting to Higher or Lower Voltage - Technical Articles, boost converter

Electronics All-in-One For Dummies, 3rd Edition ($25.00 Value