Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
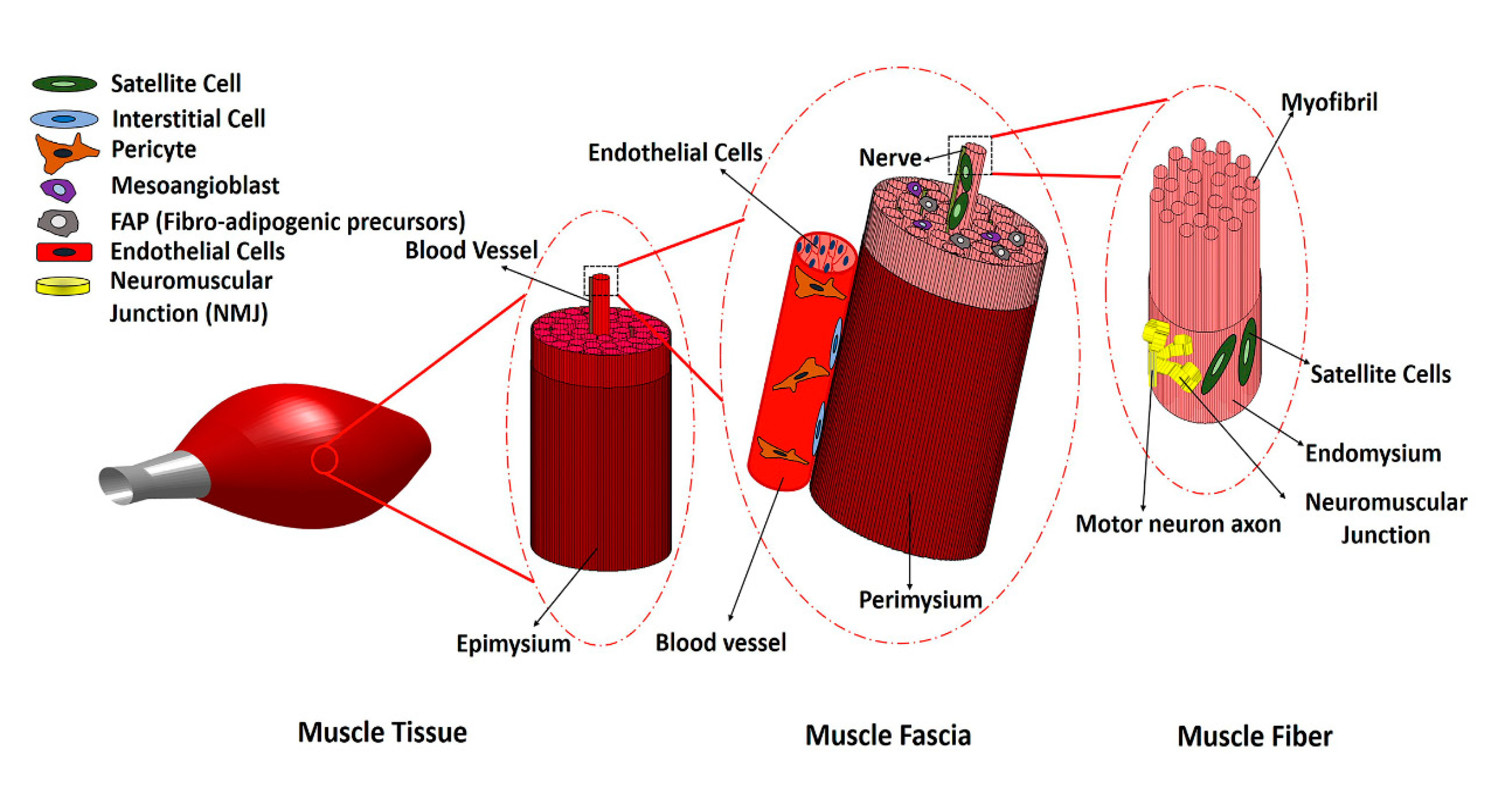
Extensive damage to skeletal muscle tissue due to volumetric muscle loss (VML) is beyond the inherent regenerative capacity of the body, and results in permanent functional debilitation. Current clinical treatments fail to fully restore native muscle function. Recently, cell-based therapies have emerged as a promising approach to promote skeletal muscle regeneration following injury and/or disease. Stem cell populations, such as muscle stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have shown a promising capacity for muscle differentiation. Support cells, such as endothelial cells, nerve cells or immune cells, play a pivotal role in providing paracrine signaling cues for myogenesis, along with modulating the processes of inflammation, angiogenesis and innervation. The efficacy of cell therapies relies on the provision of instructive microenvironmental cues and appropriate intercellular interactions. This review describes the recent developments of cell-based therapies for the treatment of VML, with a focus on preclinical testing and future trends in the field.

Yusuf Ozgur Cakmak posted on LinkedIn

MIT School of Bioengineering Sciences & Research-MITBIO

Arkansas Reports Record Ventilator Use for Second Straight Day, ventilator

Free Biomedical Engineering Intern Cover Letter Sample - Rezi
Mit School Of Bioengineering Sciences And Research Free Seminar Ad

McMaster School of Biomedical Engineering – Faculty of Engineering
Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Devices
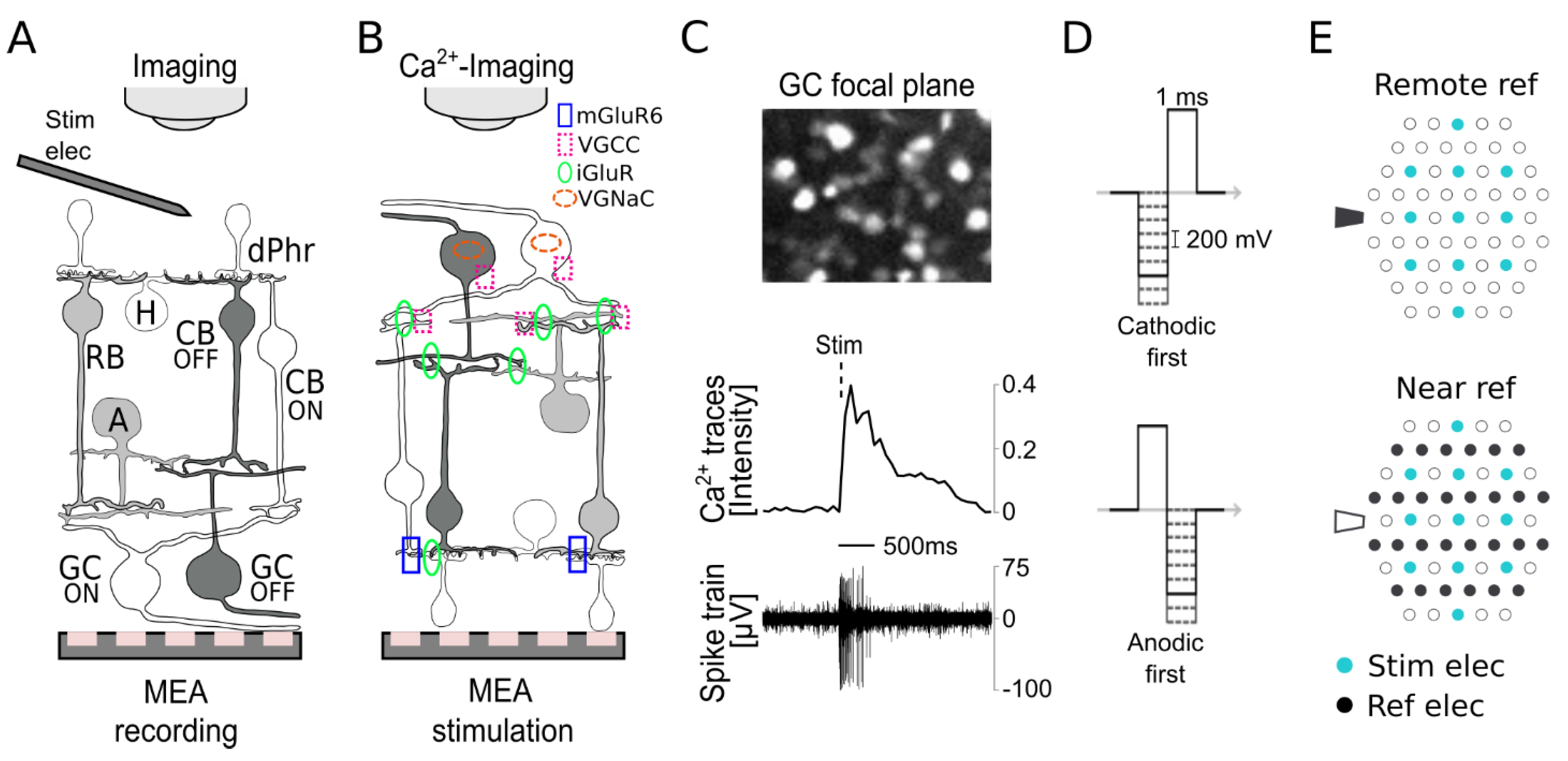
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text

3 scenarios for how bioengineering could change our world in 10 years