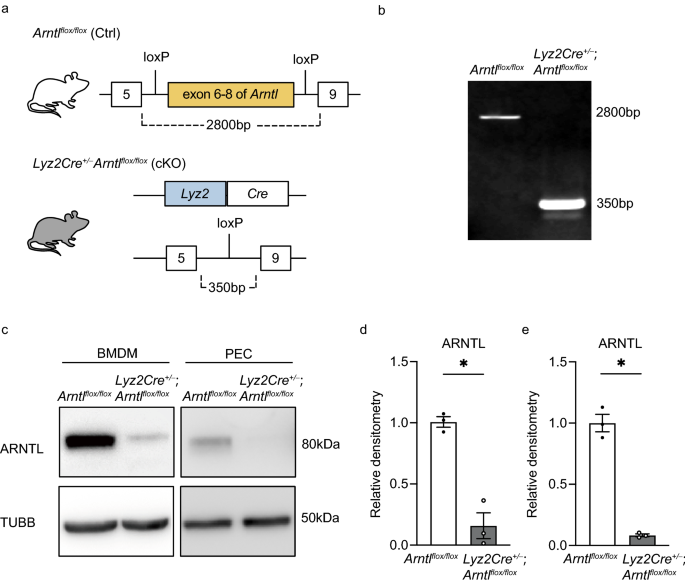
Arntl deficiency in myeloid cells reduces neutrophil recruitment and delays skeletal muscle repair

Loop Ichiro Manabe

Arntl deficiency in myeloid cells reduces neutrophil recruitment and delays skeletal muscle repair

ROS-activated CXCR2+ neutrophils recruited by CXCL1 delay denervated skeletal muscle atrophy and undergo P53-mediated apoptosis

Neutrophil and natural killer cell imbalances prevent muscle stem cell–mediated regeneration following murine volumetric muscle loss

ROS-activated CXCR2+ neutrophils recruited by CXCL1 delay denervated skeletal muscle atrophy and undergo P53-mediated apoptosis

Acute skeletal muscle injury: CCL2 expression by both monocytes and injured muscle is required for repair. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Extent of soleus (Sol) muscle atrophy induced by denervation in

Neutrophil and natural killer cell imbalances prevent muscle stem cell–mediated regeneration following murine volumetric muscle loss

PDF] Impaired ECM Remodeling and Macrophage Activity Define Necrosis and Regeneration Following Damage in Aged Skeletal Muscle

TLR2 signaling up-regulates GRK2 expression in neutrophils. ( A ) CXCR2

Muscle stem cell adaptations to cellular and environmental stress, Skeletal Muscle
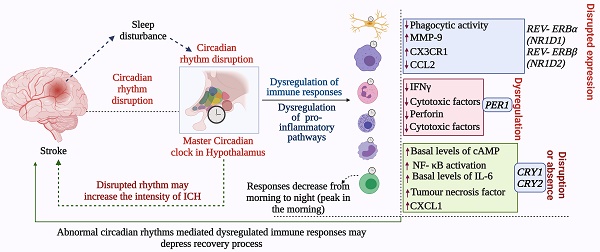
Towards improving the prognosis of stroke through targeting the circadian clock system