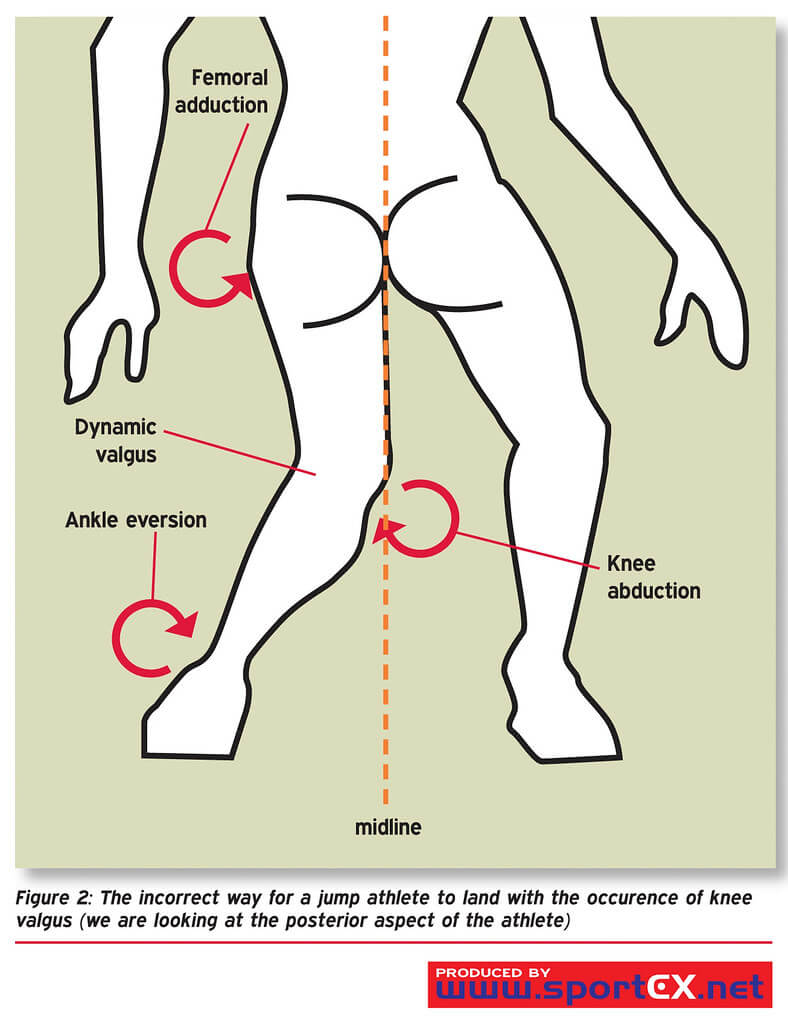
Decreased Ankle Dorsiflexion is Associated with Dynamic Knee Valgus

A proposed biomechanical explanation is that restricted ankle joint dorsiflexion directly results in overpronation of the foot, which causes internal rotation of the lower extremity, which strains the external/abductor musculature, which can then no longer prevent femoral adduction; hence genu valgus.
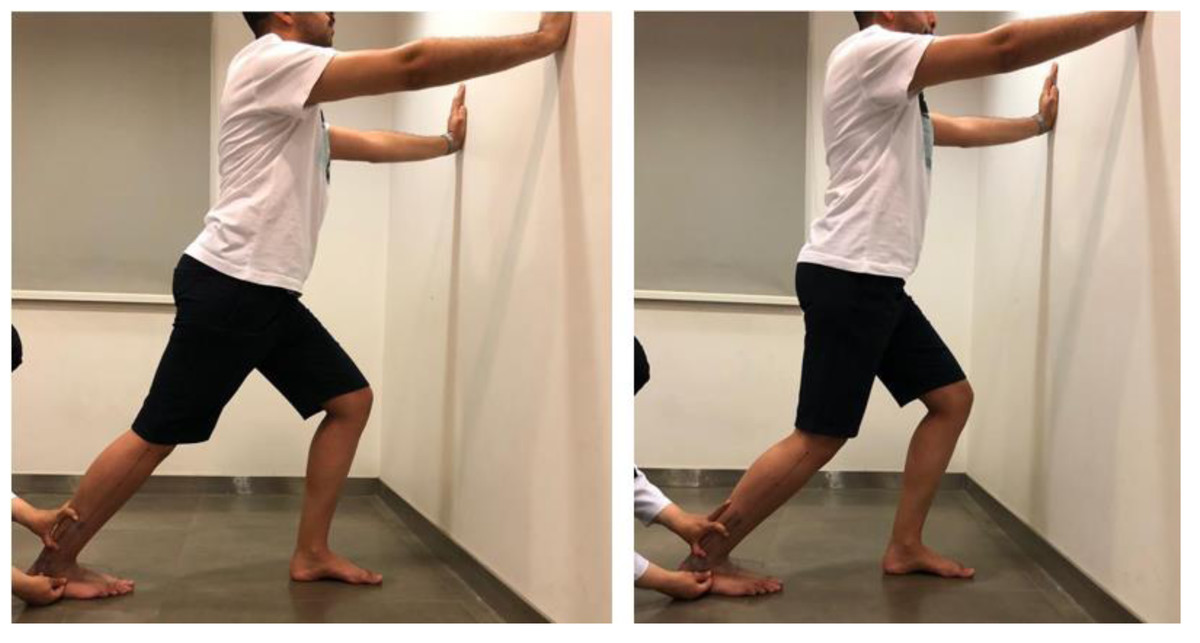
Correlation of ankle dorsiflexion range of motion with lower-limb kinetic chain function and hop test performance in healthy male recreational athletes [PeerJ]

PDF) The effect of ankle dorsiflexion range of motion in dynamic knee valgus: A systematic review

The 3 Best Ankle Mobility Exercises - Ladies Who Lift

Fratura do Tornozelo - Dr. Eduardo Pires

Collapsed arch Archives - Learn Muscles

Krankengymnastik bei Morbus Schlatter

Comparing kinematic asymmetry and lateral step-down test scores in healthy, chronic ankle instability, and patellofemoral pain syndrome female basketball players: a cross-sectional study

The relationship between ankle dorsiflexion range of motion, frontal plane projection angle, and patellofemoral pain syndrome - ScienceDirect

Total Hip Arthroplasty and Dynamic Knee Valgus

Dr. Eduardo Araujo Pires

Measurement of weight-bearing ankle dorsiflexion range of motion with
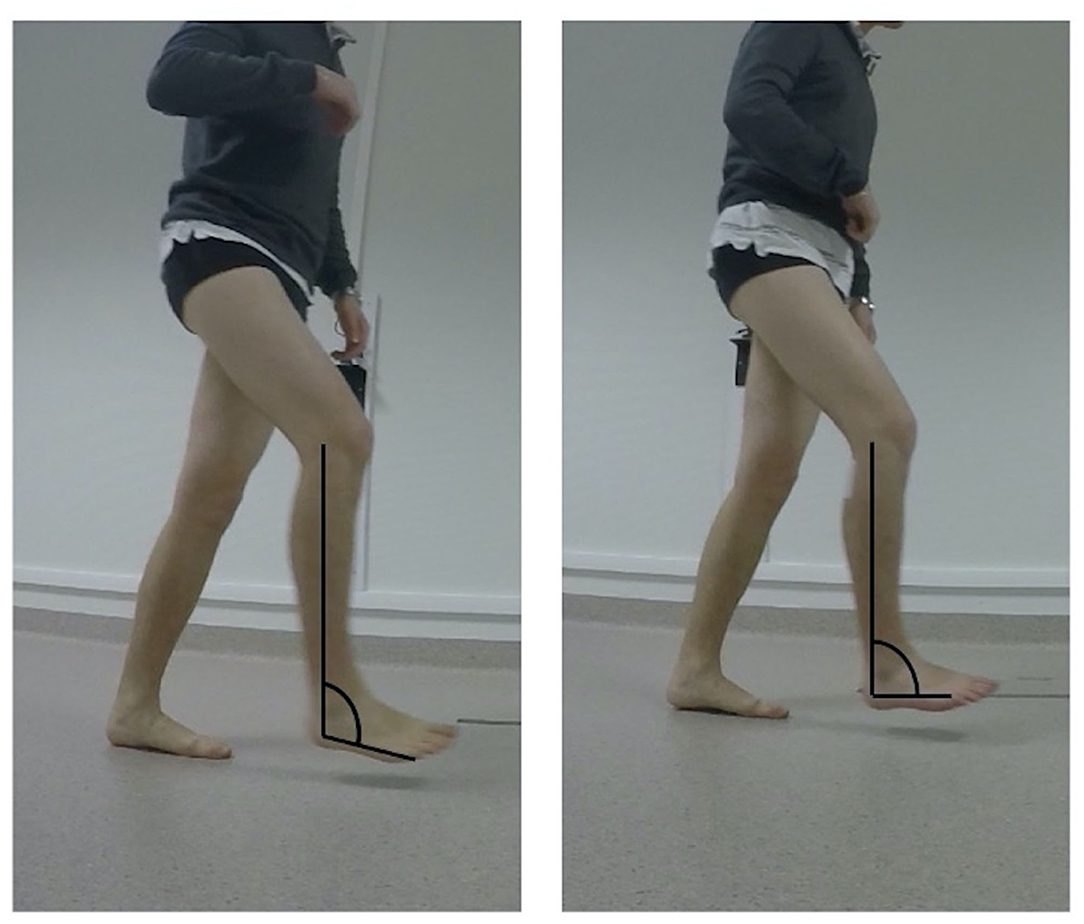
Frontiers Respective Contributions of Instrumented 3D Gait Analysis Data and Tibial Motor Nerve Block on Presurgical Spastic Equinus Foot Assessment: A Retrospective Study of 40 Adults

Decreased Ankle Dorsiflexion is Associated with Dynamic Knee Valgus
Ankle Mobility Exercises To Improve Ankle Dorsiflexion